- 关于我们
- 一站式服务
- 技术平台
临床研究
临床中心实验室
临床样本病理学检测
蛋白水平检测分析
免疫学细胞表现分型分析
药物毒性检测-CRS
TMB / 免疫微环境检测
血液疾病分型检测,类型鉴定
MRD(Minimal Residual Disease)
CART/TCRT/ADC/mAb/BisAb/
临床前研究
肿瘤疾病研究平台
小分子耐药模型
原位及转移模型
肿瘤模型 | 人源化小鼠
炎症&自身免疫疾病研究平台
脓毒症、多发性硬化症模型
炎症性肠病模型
系统性红斑狼疮、肾病模型
腹泻模型精神与神经系统:疾病研究平台
阿尔茨海默症、帕金森庄模型
疼瘾、抑郁证模型
精神分裂症、脑卒中、高血压模型
代谢疾病研究平台
肝纤维化、酒精性肝炎模型
非酒精性脂肪性肝炎(NASH)模型
急性肝损伤、肥胖模型
关节和骨疾病研究平台
关节炎、痛风,性关节炎、骨质疏松症模型
类冈湿关节炎模型
呼吸系统疾病研究平台
慢性组塞性肺病(COPD)模型
急性肺损伤模型
哮喘、肺纤维化模型
肺炎链球菌、肺支原体感染模型
肺铜绿盛染、肺曲霉感染模型
心血管系统疾病研究平台
高血压、高血脂模型
衰老、动脉粥样通化、缺血性脑损伤模型
皮肤系统疾病研究平台
银屑病、系统性硬化症模型
雄秃、斑秃模型
特应性皮炎、痤疮模型
医疗器械评价研究平台
全身毒性试验/急性、亚急性、亚慢性和慢性毒性试验
生物相容性评估
医美产品医疗器械有效性,安全性评估
药代动力学、安评
体内DMPK研究、体内DMPK研究
急毒,长毒,一般毒理
安全毒理、免疫原性评价
免疫毒性评价、非GLP毒理
- 加入我们
- 联系我们
technology PLATFORM
.png)
.png)
_30sh.png)
_z3tj.png) PROTAC的优势:
PROTAC的优势:
.png)
体外试验:
蛋白质印迹
.png)
PROTACs downregulate the protein levels of their respective targets
ELISA
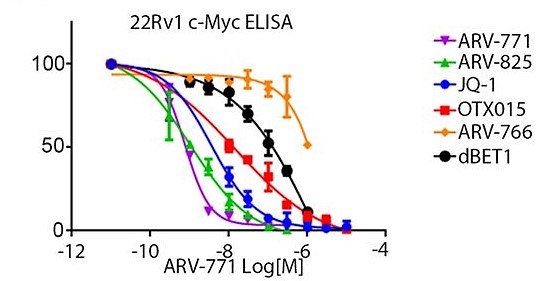
ARV-771 treatment for 16 h results in suppression of cellular c-MYC levels measured by ELISA.
IHC
.png)
Identification of the permeability of PRTC in Panc-1 cells
.png)
PRTC induces the ubiquitination and proteasomedependent degradation of the endogenous CREPT protein
Flow cytometry
.png)
Apoptosis was examined by propidium iodide (PI)/Annexin-V staining in combination with flow cytometry assay
Cell cytotoxicity
.png)
Effect of PROTAC on cell cytotoxicity
In Vivo Assays
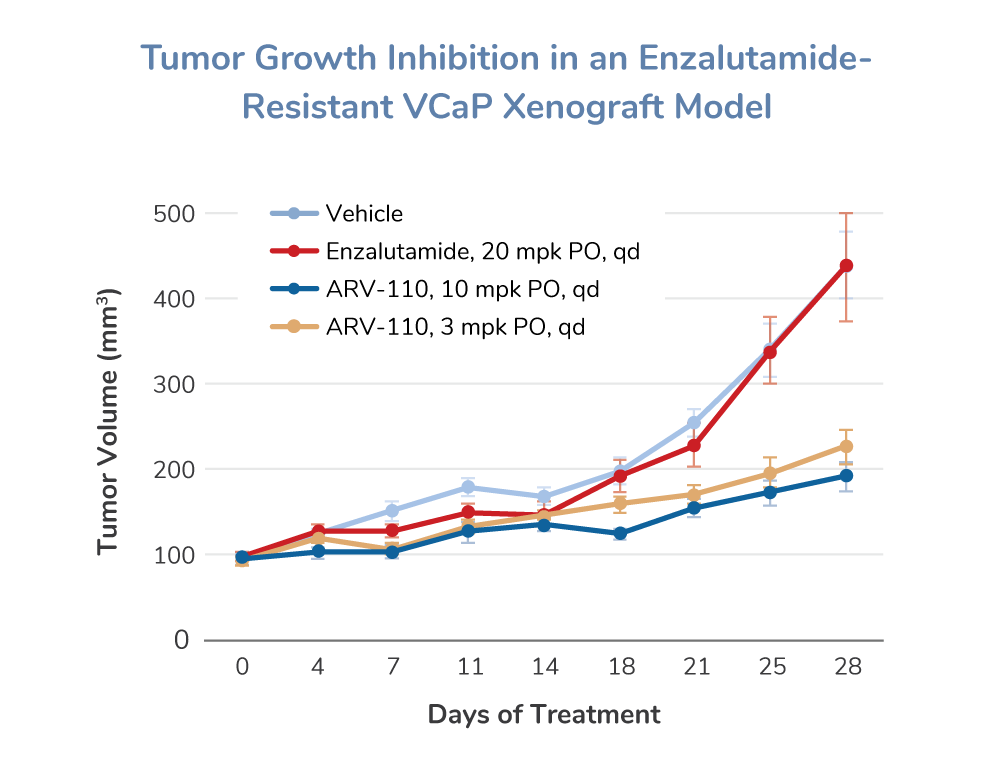
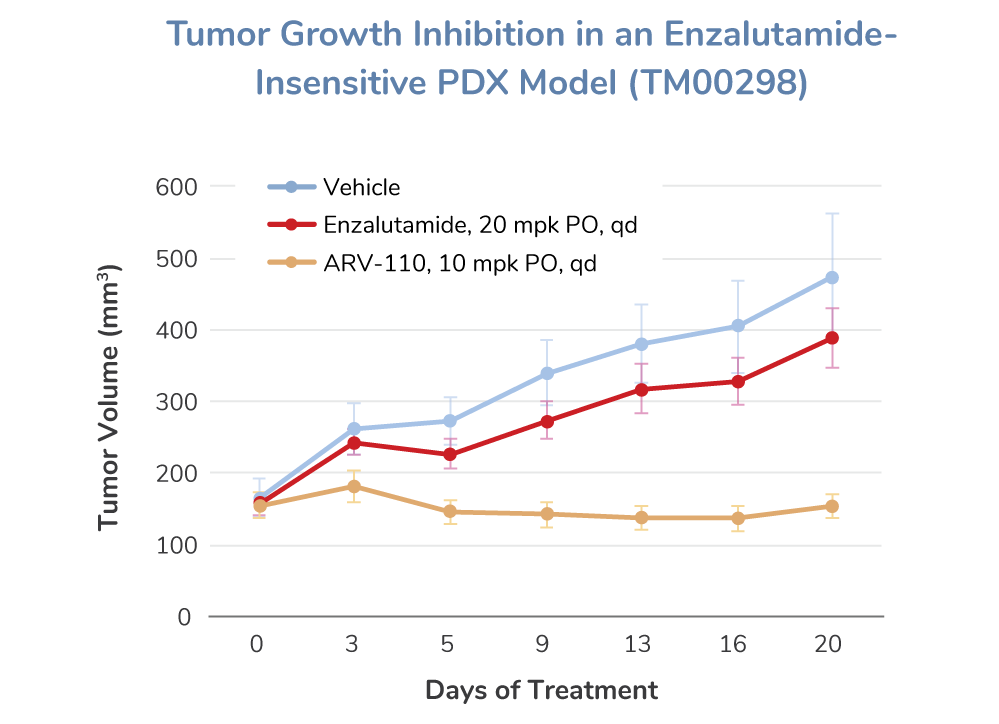
示例
Design and characterization of DCAF15 E3 ligase derived PROTAC to degrade BRD4 in vitro and in vivo
.png)
(A) PROTACs designing schematic. (B) Immunoblot of BET protein and ACTIN after 16 h of treatment of SU-DHL-4 cells with the indicated concentrations of DP1. Degradation activity is calculated below each lane as % of protein level relative to DMSO control. (C) Immunoblot of BRD4 and ACTIN after treatment of SU-DHL-4 cells with 20 μM DP1 for the indicated incubation times. (D) Left panel: Immunoblot of BRD4 and ACTIN after a 4 h pretreatment with 20 μM of ligands JQ1 and E7820, followed with a 14 h 20 μM DP1 treatment in SU-DHL-4 cells. Right panel: Immunoblot of BRD4 and ACTIN after a 4 h pretreatment with carfilzomib (0.2 μM) or MLN4924 (1 μM), followed with a 14 h 20 μM DP1 treatment in SU-DHL-4 cells. (E) Immunoblot of BRD4 and ACTIN following treatment of clone 12 and parental cells for 24 h with the indicated concentrations of DP1. (F) Cell viability analysis of SU-DHL-4 cells treated with DP1 for 48 h compared with its component ligands JQ1, E7820, and DP1(R) (n = 3). (G) Immunoblot analysis of BRD4, c-MYC, cleaved PARP and Caspase 3, and ACTIN in SU-DHL-4 cells treated with the indicated concentrations of JQ1, E7820, DP1(R), and DP1 for 24 h. (H) Tumor volume of vehicle-treated mice or mice treated with DP1 (100 mg/kg) for 12 days, n = 8. (I) Tumor weight of mice treated with vehicle and DP1 after sacrificed. (J) Immunoblot of BRD4, c-MYC, and ACTIN using tumor lysates from mice treated with vehicle and DP1
参考文献
Li, L., Mi, D., Pei, H. et al. In vivo target protein degradation induced by PROTACs based on E3 ligase DCAF15. Sig Transduct Target Ther 5, 129 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-020-00245-0
Bondeson, D., Mares, A., Smith, I. et al. Catalytic in vivo protein knockdown by small-molecule PROTACs. Nat Chem Biol 11, 611–617 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.1858
Raina, Kanak; Lu, Jing; Qian, Yimin; Altieri, Martha; Gordon, Deborah; Rossi, Ann Marie K.; Wang, Jing; Chen, Xin; Dong, Hanqing; Siu, Kam; Winkler, James D.; Crew, Andrew P.; Crews, Craig M.; Coleman, Kevin G. (2016). PROTAC-induced BET protein degradation as a therapy for castration-resistant prostate cancer. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, (), 201521738–. doi:10.1073/pnas.1521738113
Ma, D., Zou, Y., Chu, Y., Liu, Z., Liu, G., Chu, J., … Chang, Z. (2020). A cell-permeable peptide-based PROTAC against the oncoprotein CREPT proficiently inhibits pancreatic cancer. Theranostics, 10(8), 3708–3721. doi:10.7150/thno.41677
Ma, D., Zou, Y., Chu, Y., Liu, Z., Liu, G., Chu, J., … Chang, Z. (2020). A cell-permeable peptide-based PROTAC against the oncoprotein CREPT proficiently inhibits pancreatic cancer. Theranostics, 10(8), 3708–3721. doi:10.7150/thno.41677
Zhao, Qiuye; Lan, Tianlong; Su, Shang; Rao, Yu (2019). Induction of apoptosis in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells by a PARP1-targeting PROTAC small molecule. Chemical Communications, (), 10.1039.C8CC07813K–. doi:10.1039/C8CC07813K
https://www.arvinas.com/pipeline-programs/androgen-receptor
上海派思维新生物医药科技有限公司
办公地址:上海市浦东新区华夏东路333号临丰科创园5幢
人力资源 邮箱:HR@novopathway.com 电话:021-5838 0356
BD商务 邮箱:BD@novopathway.com 电话:021-5838 0618-501





